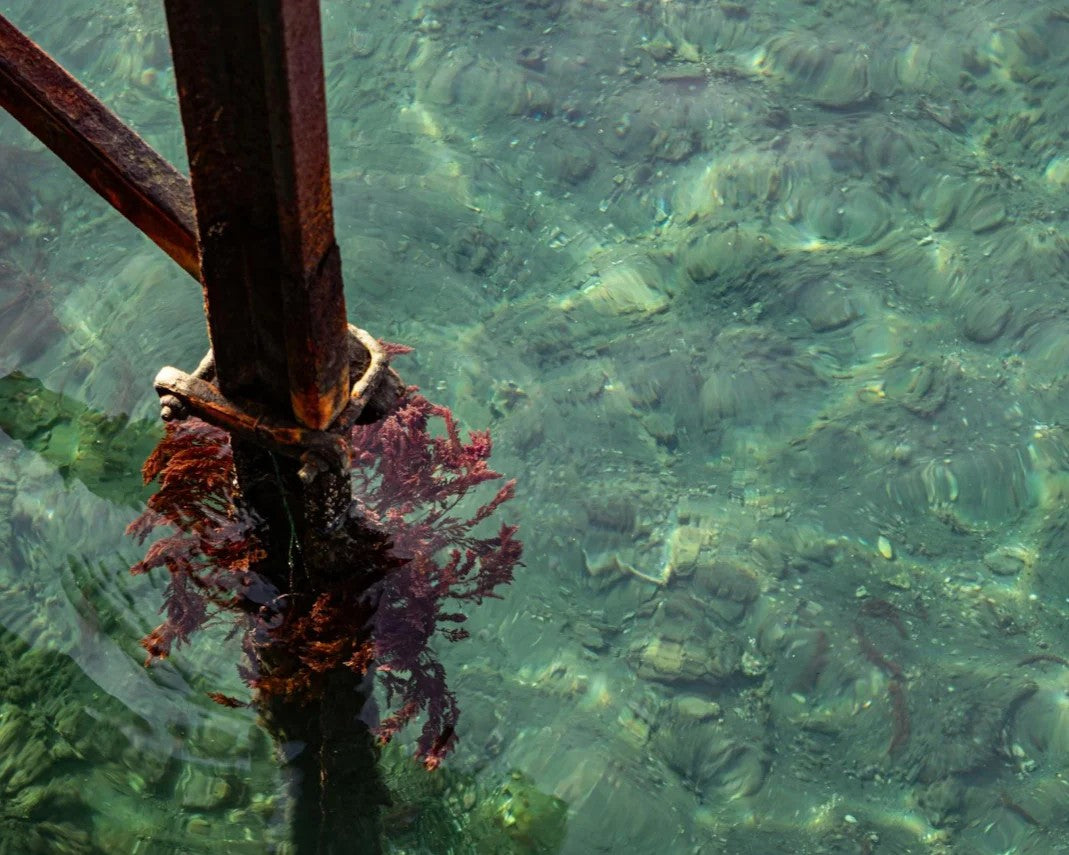
Red Algae Extract, derived from nutrient-rich marine macroalgae (Rhodophyta), is a skincare powerhouse celebrated for its antioxidant and water-binding properties. Frequently featured in hydrating and revitalizing formulations, it helps support skin’s natural moisture retention, surface smoothness, and environmental resilience.
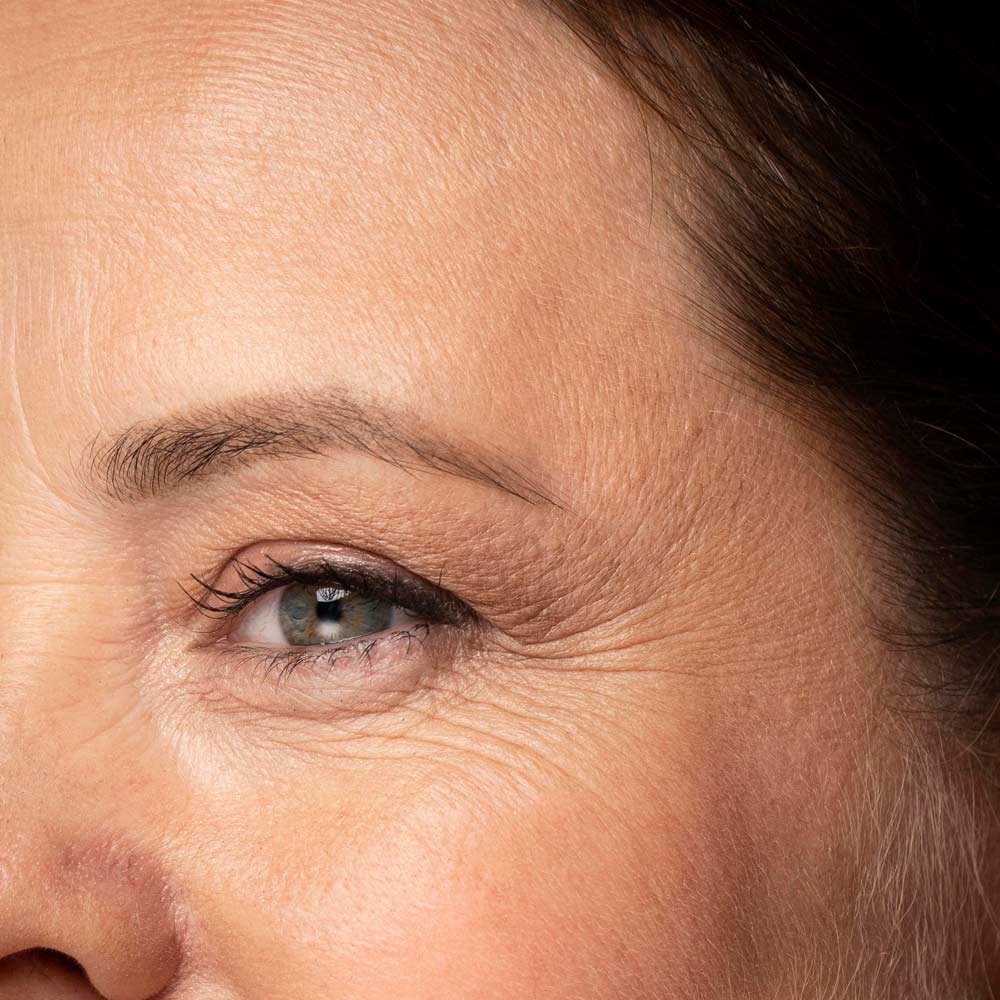
For skin undergoing midlife transitions such as dryness, dullness, or increased sensitivity, Red Algae Extract provides a gentle, marine-sourced way to restore balance and promote a visibly refreshed complexion.
A Brief History of Red Algae in Skincare
Red algae have been used for centuries in traditional coastal remedies for their soothing and restorative properties. Modern cosmetic science has since uncovered the ingredient’s impressive composition, which includes sulfated polysaccharides, minerals, peptides, and antioxidants.
Research published in the Journal of Applied Phycology,highlights that red algae’s bioactive compounds help protect the skin from oxidative stress and water loss. Today, refined red algae extracts are incorporated into skincare products that promote hydration, clarity, and visible smoothness.
How Red Algae Supports Skin During Menopause
As estrogen levels decline during menopause, the skin’s ability to retain water and maintain elasticity diminishes. This can lead to dehydration, dullness, and loss of firmness. Red Algae Extract offers lightweight topical support, helping to replenish hydration and reinforce the skin barrier.
Common Skin Symptoms During Menopause and How Red Algae Extract May Help
Dehydration and dryness: Binds moisture to the skin for improved hydration and comfort.
Weakened surface barrier: Enhances suppleness and resilience by reinforcing lipid balance.
Fine lines and rough texture: Promotes smoother-looking skin with consistent use.
Dullness or uneven tone: Revives skin radiance and supports a balanced appearance.
Environmental reactivity: Provides antioxidant protection to defend against free radical damage.
Slower recovery: Complements skin repair when used with hydrating or regenerating actives.
Studies show that marine extracts like red algae can increase skin hydration by up to 20 percent and improve barrier function, making them especially valuable for mature or hormonally shifting skin.
Visible Results with Consistent Use
With regular application, Red Algae Extract helps the skin appear more hydrated, plump, and resilient. Its bioactive marine compounds work synergistically with antioxidants and humectants in moisturizers, serums, and overnight treatments.
Because of its lightweight texture and compatibility, it’s suitable for layering and effective across most skin types, including sensitive and mature skin.
Alternative Names and Labeling Terms
Red Algae Extract may appear under several INCI (International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients) names depending on species and extraction methods:
-
Chondrus Crispus Extract (Irish Moss)
-
Lithothamnion Calcareum Extract
-
Gigartina Stellata Extract
-
Furcellaria Lumbricalis Extract
-
Carrageenan (derived from red algae)
-
Rhodophyta Extract
These refer to specific forms of red algae known for their hydrating, antioxidant, and conditioning effects.
Used in: Collagen Boosting Serum, Replenishing Night Cream
This content is for educational purposes only and is not intended to diagnose, treat, or replace professional skincare advice. For personalized guidance, please consult a licensed skincare provider.
Sources
-
Fleurence, J. (2016). Seaweed proteins: biochemical, nutritional, and functional aspects. Journal of Applied Phycology. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26971836/
-
Pallela, R., et al. (2018). Marine polysaccharides and their potential applications in skincare. Marine Drugs. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25226020/
- Kim, S. K., & Bhatnagar, I. (2011). Marine algae: Bioactive compounds and potential applications. Advances in Food and Nutrition Research. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22118871/
Read more

Japanese Tsubaki Oil, derived from the seeds of Camellia japonica, is a lightweight, non-comedogenic oil traditionally used in Japanese beauty rituals for its smoothing and nourishing qualities. Ri...

Encapsulated Vitamin E delivers the well-known protective and moisturizing benefits of Vitamin E in a stabilized, slow-release format. This advanced delivery method improves its effectiveness and s...