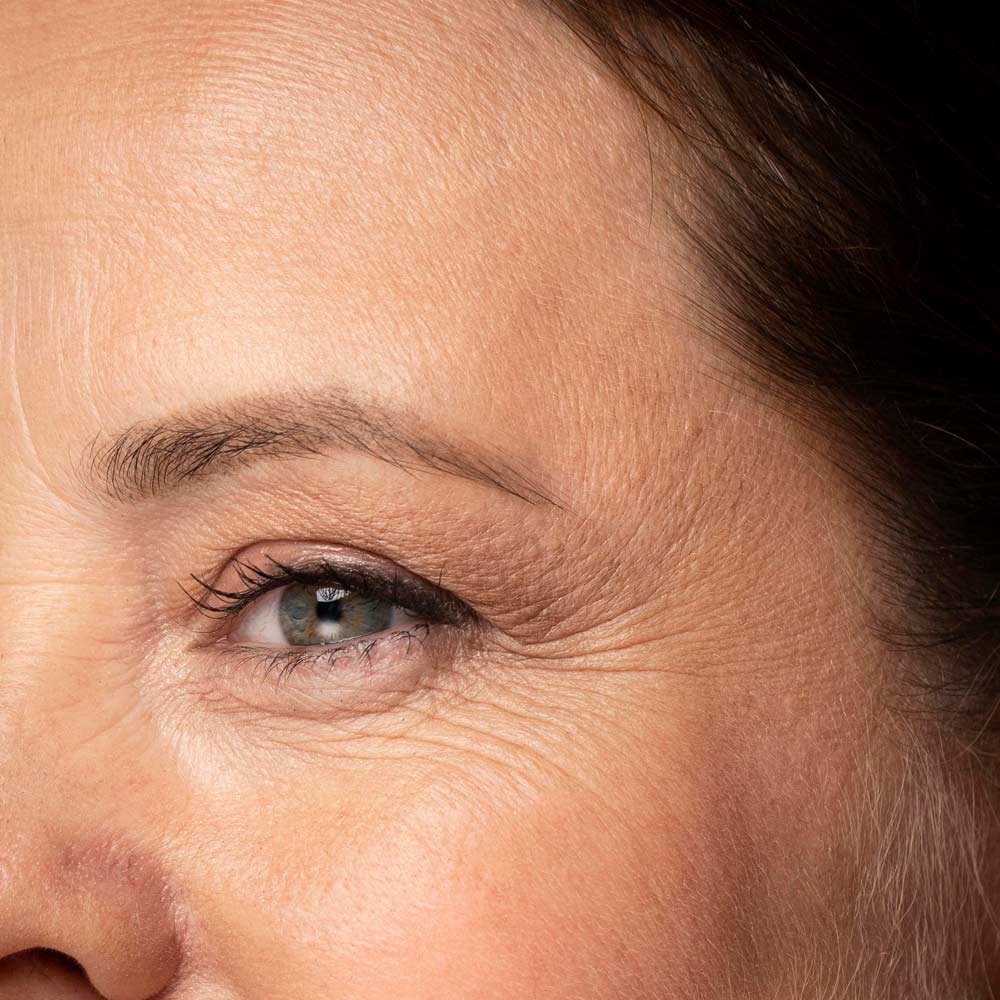
Encapsulated Vitamin E delivers the well-known protective and moisturizing benefits of Vitamin E in a stabilized, slow-release format. This advanced delivery method improves its effectiveness and skin compatibility - ideal for menopausal or mature skin that may experience dryness, sensitivity, or oxidative stress.
Known for its ability to reinforce the skin barrier and support repair, Vitamin E acts as an antioxidant shield, helping defend against environmental aggressors while promoting smoother, more resilient skin over time.
A Brief History of Encapsulated Vitamin E in Skincare
Vitamin E (often listed as tocopherol or tocopheryl acetate) has been a skincare essential for decades, valued for its antioxidant and emollient properties. However, traditional forms of Vitamin E are unstable - they degrade easily when exposed to air, heat, or light.
Encapsulation technology was developed to protect Vitamin E from oxidation until it reaches the skin, preserving potency and ensuring gradual, sustained release. By enclosing the active in lipid-based or polymeric microspheres, this method helps deliver consistent results and improves tolerance for dry, reactive, or aging skin.
How Encapsulated Vitamin E Supports Skin During Menopause
During menopause, the skin’s barrier weakens, natural oil production declines, and oxidative stress increases. This combination can lead to dryness, irritation, and dullness. Encapsulated Vitamin E helps replenish moisture, soothe sensitivity, and strengthen the skin’s protective layer - making it especially beneficial for hormonally evolving skin.
Common Skin Symptoms During Menopause and How Encapsulated Vitamin E May Help
-
Dryness and dehydration: Provides emollient support and enhances moisture retention.
-
Weakened skin barrier: Reinforces lipid layers, reducing water loss and irritation.
-
Sensitivity or irritation: Soothes inflammation through anti-inflammatory mechanisms.
-
Oxidative stress from UV or pollution: Neutralizes free radicals and supports antioxidant defense.
-
Dull or tired-looking skin: Improves surface softness and overall texture.
-
Slower recovery from stress or damage: Aids visible repair, particularly when combined with regenerative actives.
-
Fine lines and roughness: Softens texture and smooths appearance, especially when layered with peptides or Vitamin C.
Visible Results with Consistent Use
Encapsulated Vitamin E promotes comfort, smoothness, and radiance - often within days. With consistent use, it helps maintain the skin’s lipid balance, strengthens its defense against oxidative stress, and restores a sense of suppleness that midlife skin often loses.
Because of its low irritation potential, encapsulated Vitamin E pairs perfectly with other active ingredients such as Vitamin C, retinol, or hyaluronic acid, helping buffer their intensity while amplifying results.
Used in: Energizing Day Cream Tx
Sources
-
Thiele, J. J., et al. (2005). Vitamin E in human skin: Organ-specific physiology and considerations for its use in dermatology. Journal of Molecular Medicine. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16311141/
-
Papakonstantinou, E., Roth, M., & Karakiulakis, G. (2017). Hyaluronic acid: A key molecule in skin aging. Dermato-Endocrinology. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29271409/
-
Tobin, D. J. (2017). Introduction to skin aging and barrier function. Journal of Tissue Viability. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31040602/
-
Müller, R. H., et al. (2018). Encapsulation of Vitamin E in lipid nanoparticles for enhanced skin delivery. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28527508/
-
Souto, E. B., et al. (2019). Advances in encapsulation technologies for antioxidants in cosmetics. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30351683/
-
Panahi, Y., et al. (2012). Anti-inflammatory effects of topical tocopherol in skin conditions. International Journal of Cosmetic Science. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22537233/
-
Krutmann, J., & Schroeder, P. (2021). Plant peptides as novel anti-aging ingredients. International Journal of Cosmetic Science. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34930387/
- Farris, P. K., et al. (2017). Topical vitamin C and the skin: Mechanisms of action and clinical applications. Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28122774/
Read more

Red Algae Extract, derived from nutrient-rich marine macroalgae (Rhodophyta), is a skincare powerhouse celebrated for its antioxidant and water-binding properties. Frequently featured in hydrating ...

Pea Extract, derived from Pisum sativum (the common garden pea), is a nutrient-dense botanical prized for its rich protein and amino acid profile. In skincare, it’s valued for its firming, smoothin...